 Solution of the Problem of Transboundary Pollution
Solution of the Problem of Transboundary Pollution
Introduction
The current essay provides a brief description of the problem of transboundary pollution. Different countries have designed various unsuccessful initiatives directed at solving this problem. This paper will analyze the reasons of failures and provide the proposition of the new economic policy directed at the minimization of the transboundary pollution. The developed policy will be based on the application of the concepts of game theory. The current work will give thorough description of actions that should be taken for elimination of the possibility of failure of the new strategy.
Description of the Economic Problem and its Impact on Society and the Environment
One of the major characteristics of the transboundary pollution is that it can originate in one area and cause damage on another area. This characteristic is based on the ability of the harmful substances in air or water to cross borders between countries. Consequently, pollutants can be transported across thousands of miles and they harm the environment of different countries. Health of representatives of different nations becomes endangered. The major problem of transboundary pollution is that pollutants can be carried away from the heavy emitter, like a factory or the country that has various manufacturing facilities that do not use environmentally friendly solutions, and they can be deposited into countries where the amount of harmful emissions is considerably lower. Hence, the reflection of pollution, especially heavy pollution, can be found in the developed world and in remote areas like the Arctic, for example.
Nowadays, governments of different countries adapt initiatives directed at decreasing the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere in order to reduce the air pollution and decrease the greenhouse effect. For example, the emission of carbon dioxide was decreased by about 32% in the countries of the European Union from 1980 to 2000. However, some governments do not coordinate their actions directed at responding to the issue of transboundary pollution. For example, the emission of ammonia was decreased by about 27% in the European Union and, at the same time, it was increased by 3% in the USA from 1980 to 2000. Incoherent actions negate the possible positive effect on the environment, because pollution generated in the USA can be transported to Europe.
It is evident that the issue of transboundary pollution should be met by joint efforts of governments of different countries. Various initiatives, regulations, and conventions were developed and adopted. They are based on the agreements of different countries and organizations to adopt various measures for the limitation of emission of the harmful substances into the air and water. These agreements are the examples of the application of the game theory in the real life. This theory creates models of the actions of different economic players who have the aim to reach some general goal. It is based on use psychological regulatory that enables making predictions and suggesting solutions of different problems.
However, joint actions of different countries are not always successful. The example of ineffective global initiative is the realization of the Kyoto Protocol. This protocol has the aim to decrease the emission of greenhouse gasses and slow down the global warming by setting limitations on emission of harmful substances. Almost all countries in the world have fully or partly joined this treaty or adopted some of its regulations. However, the agreement has failed. This failure is reflected in the increasing of the emission of carbon dioxide: “the overall result in the global emission have no signs of slowing down”. This trend is shown on the figure 1.
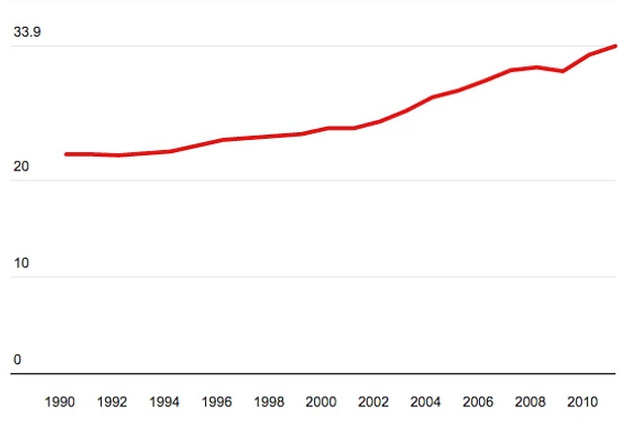
Figure 1. Change in the emission of carbon dioxide from 1990 to 2011 all over the world
It is understood that failure of the agreement is based on the unwillingness of some countries to follow the agreement or realization only the part of agreed initiatives. The realization of environment saving policies in different countries is shown on the figure 2.
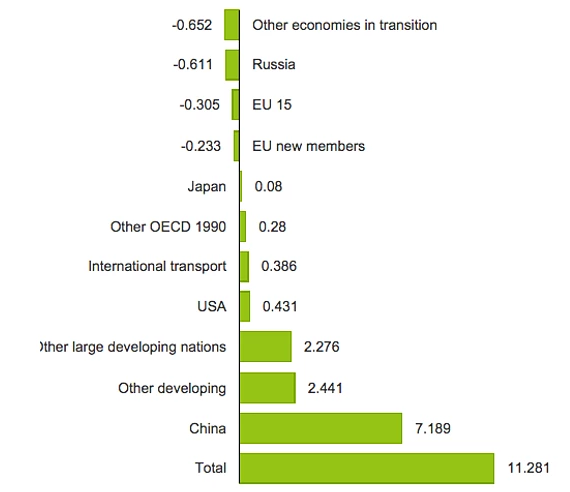
Figure 2. Change in the mission of carbon dioxide from 1990 to 2011 in different countries
The above-mentioned challenge is connected with the unwillingness of governments to put limitations of harmful emission for factories and plants situated on their territory because these actions are connected with the additional expenses on purchasing environmentally friendly equipment, lowering of production, and closing of some manufacturing facilities. This can lead to the decrease of budget revenues, growth of the cost of final production, cutting working places, and decreasing competitiveness of companies on local and international markets. At the same, time the effect from the realization of environment friendly initiatives is not immediate. It can be reflected by decreasing of the amount of harmful substances in air and water on an immense territory over time. In addition, the Kyoto Protocol has failed because this global agreement “implies a high – free incentive which is difficult to control in a global context”.
Design an Economic Policy Solution to the Problem
As it was mentioned above, the problem of transboundary pollution can be countered by joint rational actions made by the governments of several countries. Hence, the above-mentioned game theory should be applied. However, application of this economic strategy should be based on the deeper understanding of actions and behaviors of the decision-makers. It is necessary to perform a more thorough study of the game theory and its application to political and economic decisions regarding pollution. The cooperative form of the game theory is used in proposed economic policy solution. In this form, “the game players participate in a coalition and try to maximize their total welfare of the game”.
This essay contains the proposition of widening of the existing U.S.-Canada Air Quality Agreement by adding more countries that which are located on the continent such as Russia, Mexico, and Panama because these countries are also engaged in the emission of harmful substances into the air and water and spreading of these emissions all over the continent. Dangerous emissions in polluted air and water generated in one particular location are transferred all over North America by air and water. That is why this policy solution will be directed at decreasing air and water pollution through the realization of coherent and coordinated actions of all the countries located on the single continent.
The agreement will contain the requirement to reduce the sulphur content, especially from industrial sources. These sources produce the major part of the sulphur dioxide emissions. In addition, much attention will be paid to the reduction of emission of nitrogen dioxide because this substance is one of the primary precursors of acid rains. Special emission standards for vehicles and engines should be developed and realized. Large fossil fuel power plants should be engaged in initiatives of replacement of the process of coal electricity generation by the clean energy.
This agreement will have a considerable negative effect on big national and international corporations because they will be obliged to purchase and install environmentally friendly equipment instead of existing ones, develop new manufacturing guidelines directed at decreasing the emission of harmful substances, and even close some operational processes. This will lead to increasing the cost of the final production and making it less competitive on the international market. These companies will be obliged to close some of the manufacturing facilities and dismiss employees. Governments will face growth of unemployment, decrease of quality of life, and lowering of budget revenues. However, the interests of all parties involved in this small coalition will be taken into account during negotiations in order to minimize the negative effect of the implementation of environment friendly strategies. Small size of coalition will assure better meeting of challenges of each country.
Determination the Impact on the Appropriate Stakeholders
The proposed solution will require development of special regulations directed at the decrease of the amount of emitted carbon dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and other harmful substances. These regulations will affect big industrial manufacturers, fossil-fuel power plants and transportation companies (owners of vehicles) and other major producers of the harmful emissions. That is why governments should perform negotiations with representatives of these companies for the development of special procedures. These procedures should contain indemnification of expenses on purchasing of new equipment and changing of manufacturing processes necessary for decreasing the emission of the harmful substances.
This agreement will also require conscious control of emission of harmful substances by each governmental institution on the territories under their jurisdictions. Special commissions should be created for this purpose. Periodical reports of these commissions should reflect the overall trend of change in the emission of harmful substances, determine the existing problems, and contain solutions of these problems. In addition, the special intergovernmental monitoring commission should be created for observance of the realization of agreed regulations and limitations on the territory of North America. This commission should be formed from the representatives of all the countries in order to ensure the adequate and impartial monitoring. Researches of water resources, forests, plants, factories, and so on should be performed in different locations all over the continent. Outcomes of researches should be presented in quarter and annual reports. If the commission determines any inobservances, all the parties of the agreement will take joint actions directed at meeting this challenge through limitation of financing or imposing sanctions.
Much attention should be paid to the fact that the level of the economic development of Canada and the USA differs greatly from the level of economic development of Russia, Mexico, and Panama. Canada and the USA have more financial resources for effective implementation of the proposed strategy. Hence, the effective realization of environment friendly initiatives in less developed countries can be more difficult because the governments of these countries will face problems in budgeting. That is why these governments can be supported with additional financial benefits.
Analysis of the Economic Theory Used to Complete the Policy Solution
As it was mentioned above, the completion of the economic policy solution will be based on deeper understanding of the application of game theory to the issue of the transboundary pollution on the international scene. This understanding is provided by Michael Finus in his work Game theory and international environment co-operation: A survey with and application to the Kyoto – Protocol. The proposed solution contains the effective implementation of the agreed regulations by formation of a smaller coalition of countries. This will enable a more symmetric distribution of welfare and, at the same time, creation of unified and acceptable emission reduction quotas. In addition, realization of the proposed strategy will be accompanied by some form of compensation to companies and governments. The above-mentioned strategy proposes the compensation in the form of additional money support.
Michael Finus noted that the involved parties would comply with the agreement only in the case when the obtained welfare from compliance to the agreement is greater than the welfare from non-compliance with it. Consequently, considerable limitation of budgeting and imposed sanctions will ensure compliance with treated commitments. Financial stipulation is chosen as the effective instrument of safeguarding the fulfilment of the agreement because “there is slack of enforcement power on the side of donors and lack of enforcement power on the side of recipient countries”. The USA and Canada are considered as donors because their high economic development enables them to render financial assistance to countries-recipients with lower economic development (Russia, Mexico, and Panama).
How the Economic Policy Proposed would Solve the economic Problem
The proposed policy will lead to the reduction of air and water pollution on the territory of North America because all countries located on the continent will be engaged in it. Joint actions of several countries and strict control over the realization of these actions on the local and international levels will enable effective realization of the proposed agreement. This will lead to decreasing the general environmental pollution and reducing the harm to people health. The simultaneous implementation of described actions on a vast territory will increase the positive effect.
Conclusion
The current work provides description of the problem of the transboundary pollution that can be generated on one location and harm the environment on other location. The solution of this problem requires joint actions of different countries all over the world. However, signing and realization of the universal Kyoto protocol did not bring considerable results because of several reasons. Some countries have realized only part of necessary actions. Lack of strict control and adequate punishment has also led to the failure of this agreement. The solution of this challenge can be found in the creation of smaller coalitions for designation and realization of actions directed at decreasing the emission of harmful substances in the atmosphere. This will provide a more systematic distribution of welfare and, at the same time, creation of unified and acceptable emission reduction quota. At the same time, the size of these coalitions should be enough for providing relevant environmental effect. It is proposed to widen the existing U.S.-Canada Air Quality Agreement by adding other countries on the continent (Russia, Mexico and Panama).


